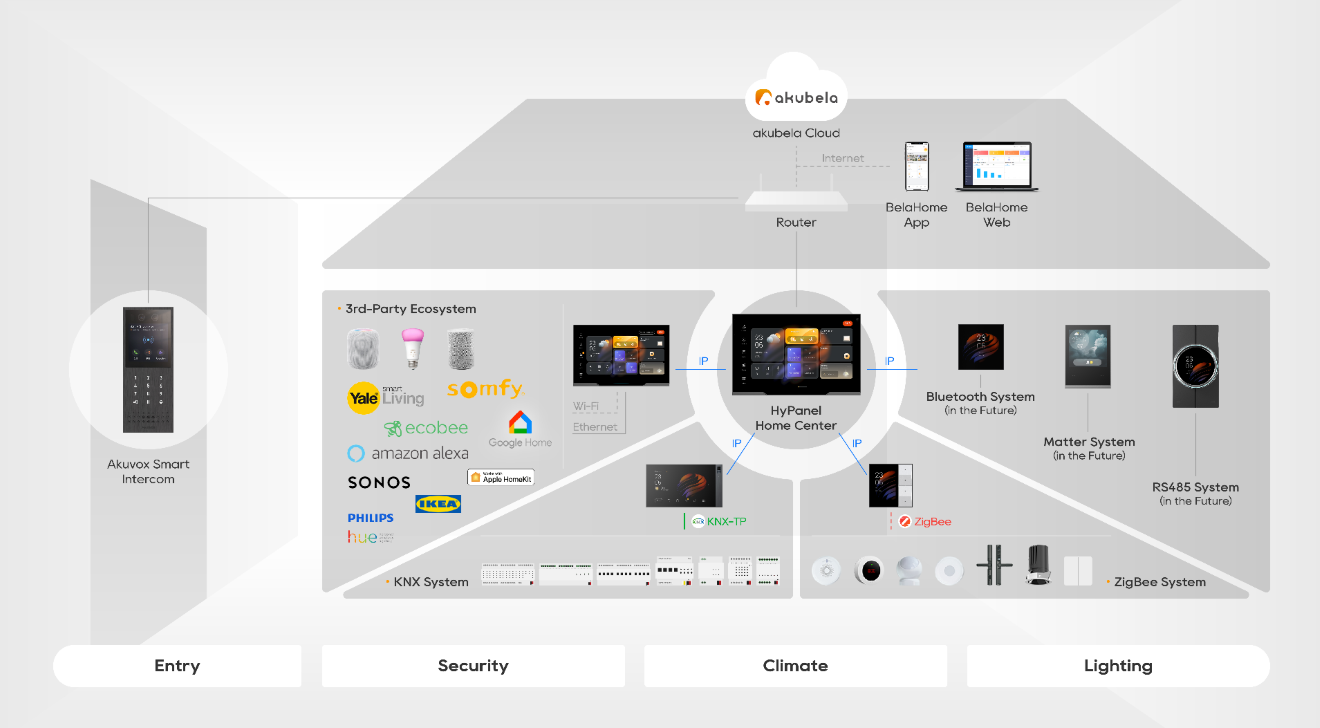
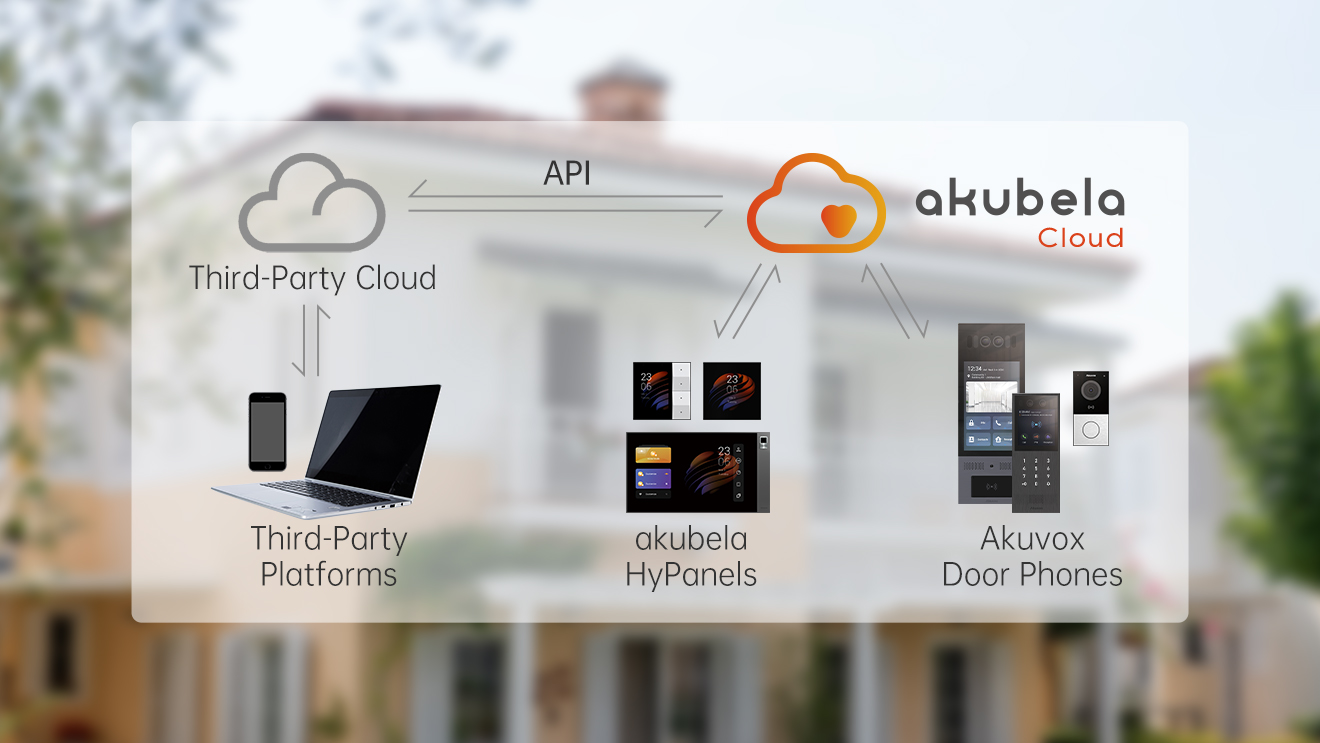
Introduction
Welcome to one of our Sites (hereinafter referred to as "the Sites"). We highly value user privacy and information protection. When you use the Sites, we may collect and use your information. Through this "Privacy Policy" (hereinafter referred to as "this policy"), we aim to clarify, in a prominent location on the Sites (at the bottom of the homepage), our business practices, the types of information we need to collect from you, the ways to access, update, and delete this information, the protective measures we have in place, and the rules we follow when sharing, transferring, or publicly disclosing your information. Please carefully read and understand this policy before using the Sites. If you do not agree with this policy, please stop using the Sites immediately. If you have any questions during the reading process, you can contact us at website@akuvox.com.
Special Statement: All akubela Sites are targeted at enterprise users. All your actions on the Sites will be considered those of an enterprise user. The information we collect through the Sites is related to your business contacts on behalf of the enterprise.
1.How We Collect Your Information
We will follow the principles of fairness, legality, and necessity, and only collect your business contact information when necessary. We adhere to the principle of data minimization to ensure that we only collect, store, and use necessary business contact information and do not exceed the scope of specific purposes (refer to the table in Section 2 for the purposes of use; if it exceeds, it requires a new risk assessment and related processes). If we intend to use your business contact information for purposes not covered by this policy or to use business contact information collected for specific purposes for other purposes, we will inform you in a reasonable manner and obtain your consent again. In addition, if you find errors in your data, you can email us at website@akuvox.com to inform us for correction.
1.1 How We Collect Your Business Contact Information:
Information You Provide Directly: We may collect and store the information you actively provide to us when using the Sites, including information you provide when filling out forms on our pages, applying for products and/or services, and contacting us for technical support.
1.2 What Business Contact Information We Collect
We follow the principle of data minimization to ensure that we only collect, store, and use necessary business contact information and do not exceed the scope of specific purposes. The business contact information we collect includes: name, title, company name, company address, company nature, work email, work phone, country, source of akubela device purchase, etc. We
recommend that you provide your corporate email, code name, and alias (avoid using personal contact information).
2. How We Use Your Business Contact Information
In order to comply with national laws and regulations and regulatory requirements, as well as to provide services to you and improve service quality, we may use your business contact information in the following situations:
| Type of Business Contact Information |
Purposes of Collection |
| Contact person, company name, work email, work phone, country, city |
1) Provide the contact person with information related to our products, solutions, technology, training, and cooperation;
2) With the permission of the business contact person, periodically send marketing information related to products, solutions, and the company to their email.
|
| Work email, country |
With the permission of the business contact person, periodically send marketing information related to products, solutions, and the company to their email. |
| Contact person, title, company name, work email, country, source of akubela device purchase |
Evaluate the distribution qualifications and authorization of the enterprise user represented by the business contact information subject or reject their distribution qualifications. |
| Contact person, title, company name, company address, company nature, work email, country, source of akubela device purchase |
Create a training account for the business contact information subject to study and assess our products and solutions on our training platform. |
| Contact person, title, company name, company address, company nature, work email, country, source of akubela device purchase |
Send a meeting link for online training on our products and solutions to the business contact information subject. |
When we intend to use your business contact information for purposes not covered by this policy or to use business contact information collected for specific purposes for other purposes, we will inform you in advance and obtain your consent in a reasonable manner. For already collected business data, unless you make specific requests, we will retain it permanently.
3. How We Use Cookies and Similar Technologies
To provide you with a more convenient browsing experience, we sometimes store small data files called cookies on your computer or mobile device. Cookies are text files stored by a web server on a computer or mobile device, and their content can only be retrieved or read by the server
that created them. Each cookie is unique to your web browser or mobile application. Cookies typically contain identifiers, site names, and some numbers and characters. Through cookies, websites can remember users' single or multiple visits (using session cookies) or preferences for settings such as language, font size, and other browsing preferences. This means that users do not need to reconfigure their preferences every time they visit a site. If a website does not use cookies, it will treat each visit by the user as a new visitor. For example, if you log in to a website and then go to another page, the website will not recognize you, and you will be logged out again.
In order to provide you with more convenient and personalized services, we provide the following services through cookies and other technologies:
(1) Analyze how you use our services. For example, we may use cookies, web beacons, and other technologies to understand the specific purposes for which you use our services or which web pages or services are most popular with you.
(2) Optimize advertising. We may display products or advertising information that you may be interested in based on statistical information about the websites you visit. This statistical information does not include any of your business contact information and may be used to assess the effectiveness of advertising. Cookies, web beacons, and other technologies help us provide targeted advertising related to the enterprise you represent rather than generic advertising.
(3) We may also use web beacon technology to compile statistics on anonymous access data. Similarly, this statistical information does not include your business contact information.
We will not use cookies for any purpose other than those stated in this policy. You can manage or delete cookies based on your preferences using your browser or device settings, which have built-in cookie clearing functions. Most web browsers automatically accept cookies, but you can usually modify your browser settings to reject cookies or delete cookies as needed. However, doing so may impact the security and convenience of your use of our services, but it will not affect your normal use of other services we provide.
4. How We Entrust Processing, Share, Transfer, and Publicly Disclose Your Business Contact Information
4.1 Sharing
We will not share your business contact information with any companies, organizations, or individuals outside of akubela, except in the following cases:
(1) With your explicit consent or authorization in advance;
(2) When required by applicable laws and regulations, mandatory administrative or judicial requirements;
(3) When necessary to provide services to you, maintain the legitimate interests, property, or safety of akubela, its affiliates, partners, you, or the public interest, we may provide business contact information in accordance with legal requirements.
(4) We will only share business contact information that is necessary to provide the services you need.
Since we collect data from you as business contact information for the purpose of business negotiations and cooperation, we may entrust authorized partners in your country to track your related business demands and send information to these partners to ensure the smooth provision of services to you. However, we will only share necessary business contact information for legal, legitimate, necessary, specific, and explicit purposes, and we will only share business contact information necessary to provide services. Our partners do not have the right to use shared business contact information for any other purpose. In addition, the Sites’ servers are provided by Alibaba Cloud. We will sign relevant data processing agreements with third-party data processors.
4.2 Transfer
We will not transfer your business contact information to any companies, organizations, or individuals unless one of the following exceptions applies:
(1) With your explicit consent or authorization in advance;
(2) In accordance with applicable laws and regulations, mandatory administrative or judicial requirements.
4.3 Public Disclosure
We will only publicly disclose your business contact information in the following circumstances, and we will do so under the premise of adopting security protection measures in line with industry standards:
(1) According to your requirements, we will disclose the business contact information you specify in a manner you explicitly agree to.
(2) In cases where it is necessary to provide your business contact information according to the requirements of laws, regulations, or mandatory administrative law enforcement or judicial requirements, we may disclose your business contact information in accordance with the types and methods of business contact information requested. Within the scope of laws and regulations, when we receive requests for disclosure of the above information, we will require the issuance of corresponding legal documents, such as subpoenas or investigation letters. We firmly believe that information requested by us should be kept as transparent as possible within the limits permitted by law. We have carefully reviewed all requests to ensure that they have a legal basis and are limited to data that law enforcement agencies are legally entitled to obtain for specific investigation purposes.
5. How We Protect Your Business Contact Information
5.1 Technical and Security Measures to Protect Your Business Contact Information
We attach great importance to the security of business contact information and take all reasonable and feasible measures to protect your business contact information:
Data Security Technical Measures: We will adopt security protection measures that comply with industry standards, including the establishment of reasonable system specifications and security technologies to prevent unauthorized access, use, modification, damage, or loss of your business contact information. The Sites use encryption technology such as Transport Layer Security (TLS) to provide browsing services via HTTPS to ensure the security of user data during transmission. akubela conducts comprehensive security control of data through information access agreements, monitoring, and auditing mechanisms. Strengthening Security Awareness: We also organize security and privacy protection training courses to enhance employees' awareness of the importance of protecting business contact information. We also require all personnel who may come into contact with your business contact information to fulfill their corresponding confidentiality obligations. Failure to fulfill these obligations may result in legal liability or suspension of cooperation with akubela.
The internet is not an absolutely secure environment, and communication methods such as email, instant messaging, and social software cannot determine whether they are fully encrypted when communicating with other users. We recommend that you use complex passwords and take care to protect the security of your business contact information when using such tools. The internet environment is not 100% secure, and we will make every effort to ensure or guarantee the security of any information you send to us.
Handling Security Incidents: To respond to risks such as business contact information leakage, damage, and loss, akubela has established multiple systems, clarified the classification and grading standards of security incidents and vulnerabilities, and the corresponding processing procedures. akubela has also established a dedicated emergency response team for security incidents, and in accordance with the requirements of security incident handling specifications, has launched security plans for different security incidents, conducted loss prevention, analysis, positioning, and formulated remedial measures, and jointly traced and cracked down on relevant departments. In the event of a business contact information security incident, we will promptly inform you in accordance with the requirements of laws and regulations: the basic situation of the security incident and possible impacts, the measures we have taken or will take, suggestions for you to take preventive measures and reduce risks, and remedies for you. We will also notify you of the relevant situation through email, letter, phone, push notification, etc. When it is difficult to notify each business contact information subject one by one, we will adopt reasonable and effective methods to issue announcements. At the same time, we will actively report the disposal of business contact information security incidents to regulatory authorities.
If you have any questions about our protection of business contact information, you can contact us through the contact information specified at the bottom of this policy. If you find that your business contact information has been leaked, especially if your account and password have been leaked, please immediately email us at website@akuvox.com to contact us so that we can take corresponding measures.
5.2 Storage of Your Business Contact Information
User data will be stored on secure and reliable servers, and necessary physical and technical measures will be taken to ensure data security. We will establish a sound access control mechanism and record and audit all access, regularly check and update security policies to ensure that our data storage solution complies with the latest security standards.
6. Your Rights
We will do our best to protect your rights. At any time, you have the right to know the situation of your business contact information that we collect and process and to supervise the measures we take. You can email us at website@akuvox.com at any time to request that we perform the above rights. We will respond to your request within thirty days after an internal assessment, take corresponding actions, and notify you of the results by email. The specific implementation methods for each right are as follows:
| Your Rights |
Implementation Method |
| Right to Know |
You have the right to know the situation of your business contact information that we collect and the way we process it. |
| Provide Information |
We will provide specific data information and processing methods in the form of data records. |
| Modification/Withdrawal of Consent |
We will add a note at the bottom of the message form to inform you that you can email us at website@akuvox.com to submit a request to modify/withdraw your consent at any time. |
| Raise Objections |
We will add a note at the bottom of the message form to inform you that you can email us at website@akuvox.com to raise objections at any time. |
| Access/Correction and/or Erasure |
We will add a note at the bottom of the message form to inform you that you can email us at website@akuvox.com to submit requests for access/correction and/or erasure at any time. |
| Notify Third Parties |
We will notify our data sharing partners of your modification/withdrawal of consent, objections, access/correction, and/or erasure requests by email, follow up with the execution of business contact information subject requests, and reply to you by email with the results. |
| Provide Copies of Business Contact Information Processing |
When you need it, we will provide you with a copy of the processing in common office software file formats. |
| Processing Requests |
After receiving processing requests, we will assess the reasonableness of the requests and notify you of the results of execution by email, execute the requests within thirty days after you confirm your agreement, and notify you of the actual execution results. |
| Automated Decision Making |
Currently, we do not make automated decisions about data, but if we do so in the future and it has a significant impact on you, we will notify you of the existence of automated decision-making, allow you to object to such decisions, and/or obtain human intervention. |
7. How This Policy Is Updated
We may modify the content of this privacy statement at any time. If you continue to use the services of this site, it means that you agree to be bound by the revised policy.
8. How to Contact Us
If you have any questions, comments, or suggestions about this policy or related matters about your business contact information, especially if you believe that our handling of business contact information has harmed your legitimate rights and interests, you can contact us at any time through website@akuvox.com. In general, we will reply within fifteen working days and complete the verification and processing.